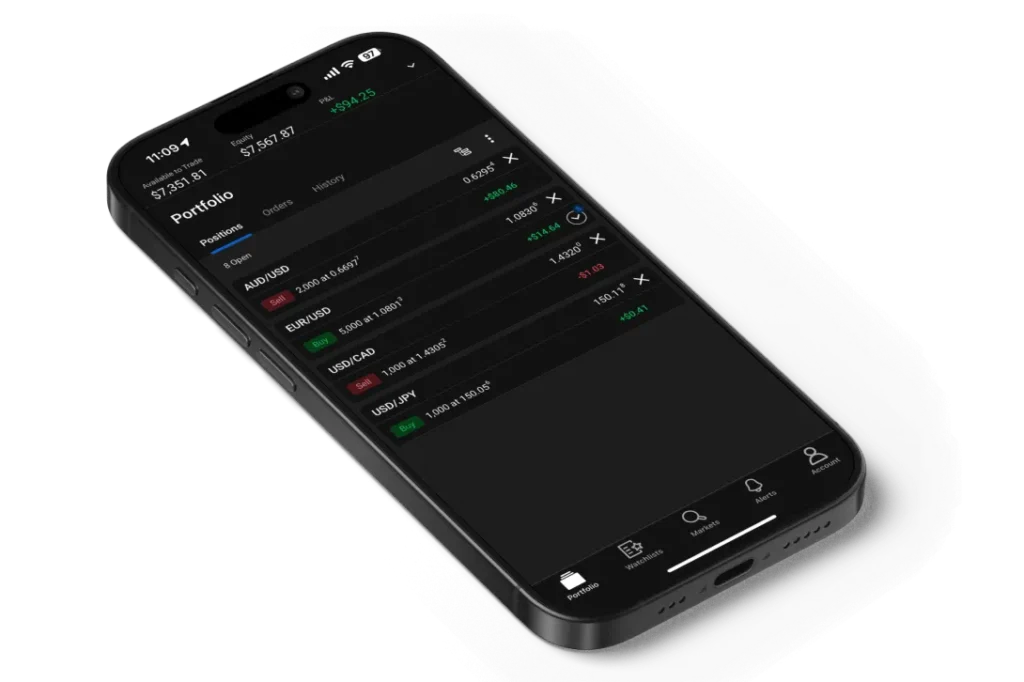
Forex trading

Forex trading

Introduction
Foreign exchange trading or Forex trading refers to the sale and purchase of currencies to achieve a profit. Being the biggest financial market worldwide, the Forex market trades over $6 trillion on a daily basis. Forex is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, unlike the traditional stock markets, and thus it is a dynamic and accessible market for traders worldwide.
This book has attempted to integrate an in-depth study of all subjects related to Forex trading, from the idea stage to strategies in detail and psychology insight.
Learning the Basic of Forex Trading
Forex trading is the trading of pairs of currencies—you sell one and buy another. For instance, with the EUR/USD pair, you’re selling dollars and buying euros. The base currency is the one named first, and the quote currency is the second.
There are three categories of currency pairs:
• Major pairs: The most highly traded currencies are included (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/USD).
• Minor pairs: Exclude the U.S. dollar (e.g., EUR/GBP, AUD/NZD).
• Exotic pairs: A main currency one and a developing or emerging market one (e.g., USD/TRY).
Key terms are:
• Bid price: Market selling price.
• Ask price: Market buying price.
• Spread: Bid-offer difference.
Key Participants in the Forex Market
Knowing who plays in the Forex market puts movement in the markets into perspective:
• Central Banks: Control value of currency using monetary policy and intervention.
• Commercial Banks: Buy and sell on behalf of clients.
• Retail Traders: Individual market players who use facilities online to bet on currency prices.
• Hedge Funds & Investment Firms: Employ Forex to hedge positions and cover investments.
• Governments: Intervene intermittently due to economic policy considerations.
How the Forex Market Functions

The Forex market operates around the clock with a network of dealers worldwide. The trading day is segmented into four main sessions:
• Sydney: Marks the beginning of the trading week.
• Tokyo: Adds to Asian market activity.
• London: Huge European hub.
• New York: Highest volume overlap with London.
Forex’s volatility and liquidity are both potential opportunities and threats. Intermediaries, such as brokers, offer platforms to enter trades and access leverage.
Fundamental Forex Terms
• Pip: Smallest variation in a currency pair price.
• Size of a trade unit (standard, mini, micro).
• Enables larger positions to be handled using lower capital.
• Capital to initiate a trade.
• Closes a trade to prevent loss.
• Closes a trade on reaching a target.
Fundamental Analysis in Forex Trading

Fundamental analysis looks at the economic, political, and financial state that affects currency rates. Some of the indicators are:
• Interest Rates: Foreign currency is attracted at higher levels.
• Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Shows economic health.
• Consumer Price Index (CPI): Shows inflation.
• Employment Reports: Register economic activity and confidence.
• Central Bank Statements: Unveil monetary policy revelations.
Technical Analysis for Forex Trading
Technical analysis entails analyzing past trends and price movements to forecast future movement. Instruments include:
• Candlestick Charts: Illustrate price movement.
• Support and Resistance: Reversal levels of prices.
• Indicators:
→ RSI (Relative Strength Index): Measures overbought/oversold.
→ MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Suggests momentum.
• Chart Patterns:
Head & Shoulders
Double Tops/Bottoms
Triangles and Flags
Forex Trading Strategies
Every trader must select a strategy that can adapt to their goals and risk tolerance:
• Scalping: Makes trades for short periods of time and gains.
• Day Trading: Trades to be opened and closed in a day.
• Swing Trading: Holds the positions for a week or longer.
• Position Trading: Trades in the long term on the basis of the macro trend.
• Range Trading: Seeks the horizontal movement of prices.
• Trend Trading: Observes the direction of the market.
Risk Management in Forex

Risk Management safeguards your capital and guarantees long-term profitability:
• Risk-to-Reward Ratio: Profit vs possible loss.
• Position Sizing: How much to invest.
• Stop-loss Orders: Automatically cap losses.
• Diversification: Averages risk between trades.
• Avoiding Over-Leveraging: Prevents huge losses.
Forex Trading Psychology
Emotional control is vital with Forex:
• Fear and Greed: Lead to irrational behavior.
• Discipline: Sticking to your plan.
• Patience: Waiting for optimal circumstances.
• Confidence vs Arrogance: Familiarity with your game plan vs over-trading.
Opening a Forex Trading Account
How to open trading account:
• Choose a Broker: Check they are regulated.
• Open Account: Fill out KYC documents.
• Fund Your Account: Opt for secure payment methods.
• Select Account Type: Standard, mini, micro.
• Demo Trading: Practice first before live trading.
Trading Platforms (MT4, MT5, cTrader)
Successful trading platforms will have analysis tools and execution tools:
• MetaTrader 4 (MT4): Easy to use, great support.
• MetaTrader 5 (MT5): Powerful features.
• Trader: Order management, contemporary UI.
Most important features:
• Customizing charts
• Automated trading (EAs)
• risk management tools
Advanced Forex Tools and Resources
To gain an edge:
• Trading Bots & EAs: Trade strategies automatically.
• Copy Trading: Replicate professional traders.
• Economic Calendars: Follow key events.
• News Sources: Bloomberg, Reuters, ForexFactory.
• Trading Communities: Social networks and forums.
Legal & Regulatory Aspects of Forex Trading
Comprehending the legal framework prevents scams:
• Regulated Brokers: Ensure investor protection.
• Licensing Bodies:
o FCA (UK)
o CySEC (Cyprus)
o CFTC (US)
o ASIC (Australia)
• Taxes: Country-specific—record profits for accurate reporting.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Forex Trading
Steer clear of these pitfalls:
• Chasing Losses: Causes impulsive trading.
• Ignoring Risk Management: Heightens exposure.
• Overtrading: Depletes your capital.
• Lack of a Trading Plan: Results in inconsistency.
• Blindly Following Signals: Always confirm.
Creating a Successful Forex Trading Plan
A good plan entails:
• Trading Objectives: Set short and long-term goals.
• Strategy Development: Select what suits you.
• Backtesting: Try on historical data.
• Journaling: Keep records and review performance.
• Continuous Learning: Markets evolve so should you.

Conclusion and Next Steps
Forex trading needs time, discipline, and ongoing learning. Provided you have a proper knowledge of technical as well as fundamental analysis, risk management, and discipline, you will find it easy to trade in the largest financial market of the world. Begin with a demo account, develop a trading plan, and move towards live trading gradually while always upgrading your skill set. To understand broader market movements, you can also check our guide on the Dow Jones and Stock Markets. For more in-depth insights, refer to this Pacerline Forex Resources. If you stick to it, you can make Forex trading a successful economic enterprise.





